First published in The Wire
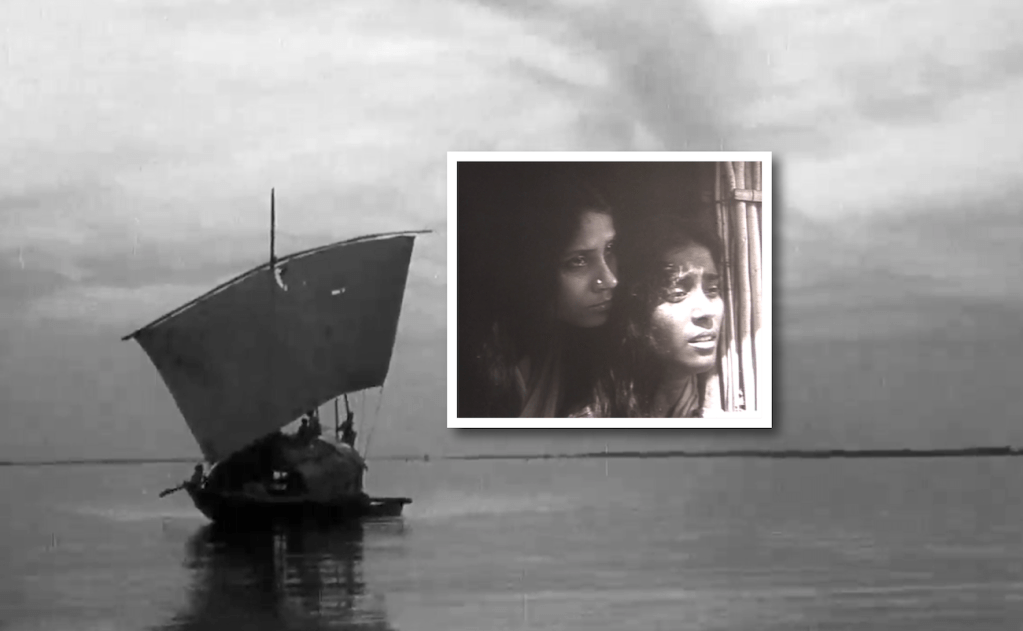
Night falls on a river. The village around it thickens with darkness. Not the river. On its breast, distant lights flicker like inextinguishable fireflies. The glow comes from the boats of the fishermen sailing on its waves. A majhi (boatman) sings a drawn-out tune and the river’s water folds into its haunting essence with every splash of the oar.
This is how the 1959 Pakistani film, Jago Hua Savera (The Day Shall Dawn) unfolds as does Padma Nadir Majhi (The Boatman of Padma), the novel it’s adapted from. An enthralling flute amplifies the aural impact of Jago Hua Savera’s opening scene even more, holding the viewer in a delicate trance. A synthesis of the work of stalwarts like Faiz Ahmed Faiz who wrote the songs, dialogues and story; music director, Timir Baran and Academy Award winning cinematographer, Walter Lassally – this first scene establishes the tenor of the film’s sensitive and neo-realist aesthetic.
That the night isn’t pitch-black isn’t insignificant. Like the Padma itself, it is mysterious and pregnant with possibility. Of light. Of dawn. It has to be that way. For the Padma is as unforgiving to the fisherfolk edging its banks as it is giving.
When Manik Bandopadhyay wrote Padma Nadir Majhi, his sparkling novel chronicling the lives of East Bengal’s fishermen, India was under British rule and the Second World War was still three years away. When director A.J. Kardar adapted it for the screen, Partition had split India, and Faiz’s reworked story reflected the region’s altered geopolitics. Filmed on location at Saitnol on the banks of the Meghna River in what was then East Pakistan, the film’s story marks a significant, and arguably necessary, departure from the novel.
The biggest change is also the most awkward one – the fisherman’s tongue. Instead of the regional Bangla dialect of the book, the characters in Jago speak in colloquial Hindustani. It’s not an A for B transposition, though. For me, a Bengali married to a Sikh, the ingenious workaround Faiz and Kardar employed to get around the language hurdle struck a personal resonance. Despite speaking fairly respectable Hindi all my unmarried life in Delhi, my hometown, with my husband, I started speaking in a deliberately incorrect tongue, upturning verb conjugations – a pattern absent in Bengali.
The fishing villagers of Jago speak a similar broken Hindustani, their vocabulary sparse and uncluttered. When the viewer is least expecting it, fragments of Bengali float into her ears – a kid begging his father to spare “duto poisa,” another telling his uncle, “Miyan boddi anchhe,” (the miyan has brought a traditional doctor), and then a full exchange in Bangla between two sisters, Tripti Mitra playing the younger of them.
An idiom for celluloid
One would be mistaken, however, in attempting to locate the film’s vocabulary in a particular vernacular. From the first scene to the concluding one, the elements that dominate both the stylistic and utilitarian purposes of Jago are wordless – the music, the ambient sounds, the silence. In the opening scenes, the viewer gets a sense of a sound peculiar to Padma’s boatmen as Bandopadhyay describes it:
“From the heart of the river afar, a call is heard, a faint sound of human voice…This is a language known only to the boatmen of East Bengal. There are no words in this language, only undulating vocalization. Across unbounded horizons spreading over the river, this sound travels long distances, becoming fainter in volume, but unchanged in its ripples.” [From Padma Nadir Majhi, translated by the author.]
The depth and breadth of Timir Baran’s prowess as a composer are on full showcase here, not just in the three songs that a boatman sings, all carrying the resilient poise of Faiz’s poetry, but also in the music director’s unusual choice of the classical veena – to overlay everyday village scenes with a sedate composure.
Then there are atmospheric sounds – the Padma’s waves, of course, but also the chatter of kids playing on its banks, the cawing of crows, the buzz of a bustling fish market and, later in the film, the big city’s honking automobiles, hawking porters and tinkling bicycles – that lend the narrative a compelling immediacy.
Lassally’s mature camerawork makes it even easier for the director to stick to verbal minimalism in the film. From the first frame, the camera moves with eloquence to capture both nature and man. While the Padma’s expanse and excitability are made almost palpable for the viewer, the close-ups of the characters’ faces strike one as archives of an ancient sadness.
In Jago, the majority of the villagers are Muslims as opposed to the Hindus in the novel. The characters and the plot are a lot less complex, too, making this nearly an original story, written for a new audience.

Most noticeable among the revised characters is that of Bandopadhyay’s Hossain Miya, an enigmatic man of wealth who could be caring or ruthless, depending on the situation. In Jago, he becomes the unidimensional Lal Miyan, a moneylender like any other, stripped of complexities.
The other big character swap is that of the protagonist’s sister-in-law’s. The novel’s Kapila is Mala in the film, played with sensual charm by Tripti Mitra. As in the book, she retains her flirtatious ways, but instead of enticing Miya, her brother-in-law, is seen to attract the attention of Kasim, Miya’s brotherly friend. Bangladeshi acting legend, Khan Ataur Rahman not only plays the role of Kasim with self-assurance, but also sings the film’s songs with tender facility. Particularly enduring is his rendition of “Beet chali hai raat/ab chhoro gham ki baat,” (The night is about to end, my friend/Let go of your songs of sorrow), a spirited nazm by Faiz that Baran has set – to an electrifying effect – to a traditional bhatiyali tune.
Of deprivation and the dawn of hope
There is less gossip and innuendo in the film, too, the extent of it being Lal Miya pointing fingers at Kasim and Mala’s open show of affection for each other. Yet, despite all these deviations, the film remains faithful to Bandopadhyay’s work in a fundamental way – in its politics.
At the core of Padma Nadir Majhi is the social discrimination, ostracism and extreme poverty the fishermen suffer. Their destitution is naked, for they have little to cover it with. But it’s still not without dignity. Miya pulls a fragile cover over his newborn son and helps his invalid wife lie down beside him with the gentlest touch. When his daughter’s leg is fractured, Kasim lifts her in his arms and takes her for treatment to the city hospital – a long and arduous journey he undertakes without a blink. Ganju, obsessed with buying a new boat off Lal Miyan, saves every penny for it despite seeing tuberculosis sniffing the life out of him.
Despite its affirmative title, Jago Hua Savera is rooted in reality. Ganju will acquire his boat but not live long enough to enjoy it. Miya will not be able to buy it, not even after collecting all his life’s savings, including the money his wife has been saving for their daughter’s wedding, the pennies in his son’s piggy bank and Kasim’s offered savings. Wistfully, and in his torn vest, he’ll keep his gaze on the treasured boat as it floats on Padma’s bosom.
And still the fisherfolk will wrest their dawn from the night – the Padma will hold them in her sway again, Miya will approve of Kasim’s relationship with Mala, and Kasim and Miya will return to the fishing boat. And the glow of its lantern.
This is a dawn that’s as unremarkable as the fishermen’s’ lives. It is still a savera, nonetheless.
Jago Hua Savera is a landmark film, not only because of its international cast and crew or the way it draws inspiration from the best of world cinema. But because it reinvents a classic in its own, cinematic, idiom.
[The Day Shall Dawn (1959) was selected as the Pakistani entry for the Best Foreign Language Film at the 32nd Academy Awards, but was not accepted as a nominee. It was also entered into the first Moscow International Film Festival where it won a Golden Medal. Days before the film was to premier, the new government of Pakistan (under Ayub Khan) asked the film’s producer, Nauman Taseer not to release the film. The writer, Faiz Ahmad Faiz, was later imprisoned by the government for his communist beliefs. Anjum Taseer, son of the producer, had the film fully restored in 2010.]